Uterine Fibroids: All you need to know
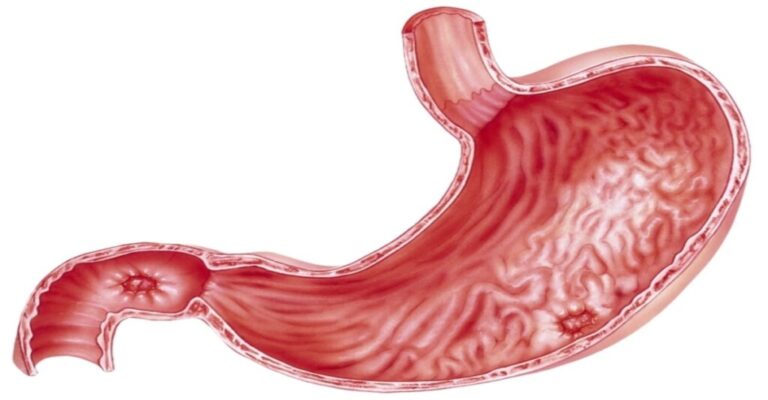
Fibroids are abnormal growths that develop in or on a woman’s uterus. Sometimes these tumors become quite large and cause severe abdominal pain and heavy periods. In other cases, they cause no signs or symptoms at all. The growths are typically benign, or noncancerous.
Fibroids are also known by the following names:
- leiomyomas
- myomas
- uterine myomas
- fibromas
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), about up to 80 percent of women have them by the age of 50. However, most women don’t have any symptoms and may never know they have fibroids.
Types of fibroids
The type of fibroid a woman develops depends on its location in or on the uterus.
Intramural fibroids Intramural fibroids are the most common type of fibroid. These types appear within the muscular wall of the uterus. Intramural fibroids may grow larger and can stretch your womb.
Subserosal fibroids Subserosal fibroids form on the outside of your uterus, which is called the serosa. They may grow large enough to make your womb appear bigger on one side.
Pedunculated fibroids
Subserosal tumors can develop a stem, a slender base that supports the tumor. When they do, they’re known as pedunculated fibroids.
Submucosal fibroids These types of tumors develop in the middle muscle layer, or myometrium, of your uterus. Submucosal tumors aren’t as common as the other types.

What Causes fibroids?
It’s unclear why fibroids develop, but several factors may influence their formation.
- Hormones
Estrogen and progesterone are the hormones produced by the ovaries. They cause the uterine lining to regenerate during each menstrual cycle and may stimulate the growth of fibroids. - Pregnancy
Pregnancy increases the production of estrogen and progesterone in your body. Fibroids may develop and grow rapidly while you’re pregnant.
Who is at risk for fibroids?
Women are at greater risk for developing fibroids if they have one or more of the following risk factors:
- Pregnancy
- A family history of fibroids
- A high body weight
Symptoms
Your symptoms will depend on the number of tumors you have as well as their location and size. For instance, submucosal fibroids may cause heavy menstrual bleeding and trouble conceiving. If your tumor is very small or you’re going through menopause, you may not have any symptoms.
Fibroids may shrink during and after menopause. This is because women undergoing menopause are experiencing a drop in their levels of estrogen and progesterone, hormones that stimulate fibroid growth.
Symptoms also include:
- heavy bleeding between or during your periods that includes:
blood clots
pain in the pelvis or lower back
increased menstrual cramping
increased urination
pain during intercourse
menstruation that lasts longer than usual
pressure or fullness in your lower abdomen
swelling or enlargement of the abdomen
Uterine fibroid is a common concern in women at fertile age causing multiple bleeding and pain symptoms which can have a negative impact on different aspects in women’s life. Fibroid has been strongly linked to hormonal imbalance which is caused by Oxidative stress due to deficiency of Glutathione in the liver. The liver is responsible for the removal of excess hormones and balancing of the hormones but it strong depends on Glutathione to do that.
Suggestion
Glutathione is the strongest antidote for oxidant stress which maximizes the liver function. And Cellgevity boosts glutathione 300% better than the best alternative.
Once the liver’s glutathione levels are raised the liver will remove the excess estrogen and balance progesterone and testosterone and the fibroid will shrink naturally.
Omega oils especially Omega 3 oil has been Scientifically known for its ability to stop tumor growth. So, adding Max 357 with Cellgevity brings a faster result. Results are not typical and fully depends on the body metabolism and size of the tumor.
If the size is big, we strongly recommend surgery but you can use Cellgevity to hasten the recovery and prevent further occurrence. Surgery brings fast relieve but doesn’t give permanent solution because it doesn’t balance the hormones responsible for the growth and that’s why many go back for several surgeries.