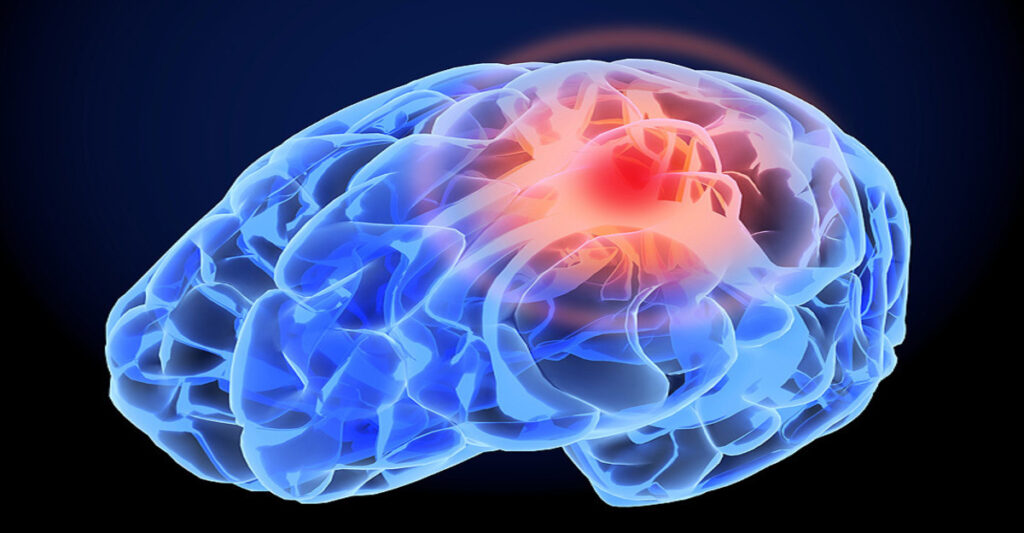
Stroke
Stroke occur when the supply of blood to the brain is either interrupted or reduced. When this happens, the brain does not get enough oxygen or nutrients, and brain cells start to die.
World-wide approximately 40 percent of people who die from stroke are males, with 60 percent of deaths occurring in females. According to the American Heart Association (AHA), Stroke is the 2nd leading cause of death in the world.
Types of Stroke
Ischemic Stroke:
Ischemic stroke occurs when a vessel supplying blood to the brain is obstructed. It accounts for about 87 percent of all strokes.
The build-up of fats, cholesterol and other substances in and on the artery walls are the main cause for ischemic stroke.
Fatty deposits can cause two types of obstruction:
Cerebral thrombosis is a thrombus (blood clot) that develops at the fatty plaque within the blood vessel.
Cerebral embolism is a blood clot that forms at another location in the circulatory system, usually the heart and large arteries of the upper chest and neck. Part of the blood clot breaks loose, enters the bloodstream and travels through the brain’s blood vessels until it reaches vessels too small to let it pass. A main cause of embolism is an Irregular Heartbeat (Atrial fibrillation). It can cause clots to form in the heart, dislodge and travel to the brain.
Hemorrhagic Stroke
Hemorrhagic strokes make up about 13 percent of stroke cases. It’s caused by a weakened vessel that ruptures and bleeds into the surrounding brain. The blood accumulates and compresses the surrounding brain tissue.
A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a weakened blood vessel ruptures. Two types of weakened blood vessels usually cause hemorrhagic stroke: An excessive localized swelling of the wall of an artery (Aneurysms) and an abnormal connection between arteries and veins, usually in the brain or spine (Arteriovenous).
Fast facts on stroke:
During a stroke, the brain does not receive enough oxygen or nutrients, causing brain cells to die.
Strokes need to be diagnosed and treated as quickly as possible to minimize brain damage.
Treatment depends on the type of stroke.
The most effective way to prevent strokes is through maintaining a healthy lifestyle and treating underlying conditions that could be a risk factor.
Causes
Most of all these causes are as a result of oxidative stress. You can treat some conditions that make you more likely to have a stroke.
High blood pressure: Your doctor may call it hypertension. It’s the biggest cause of strokes.
Tobacco: Smoking or chewing it raises your odds of a stroke. Nicotine makes your blood pressure go up. Cigarette smoke causes a fatty buildup in your main neck artery. It also thickens your blood and makes it more likely to clot. Even secondhand smoke can affect you.
Heart disease: This condition includes defective heart valves as well as an irregular, often rapid heart rate that commonly causes poor blood flow, or irregular heartbeat, which causes a quarter of all strokes among the very elderly. You can also have clogged arteries from fatty deposits.
Diabetes: People who have it often have high blood pressure and are more likely to be overweight. Both raise the chance of a stroke. Diabetes damages your blood vessels, which makes a stroke more likely. If you have a stroke when your blood sugar levels are high, the injury to your brain is greater.
Weight and exercise: Your chances of a stroke may go up if you’re overweight. You can lower your odds by working out every day.
Medications: Some medicines can raise your chances of stroke. For instance, blood-thinning drugs, which doctors suggest to prevent blood clots, can sometimes make a stroke more likely through bleeding. Studies have linked hormone therapy, used for menopause symptoms like hot flashes, with a higher risk of strokes. And low-dose estrogen in birth control pills may also make your odds go up.
Age: Anyone could have a stroke, even babies in the womb. Generally, your chances go up as you get older. They double every decade after age 55.
Family: Strokes can run in families. You and your relatives may share a tendency to get high blood pressure or diabetes. Some strokes can be brought on by a genetic disorder that blocks blood flow to the brain.
Here are 11 things you can do to stay stroke-free:
- Know and control your blood pressure.
- Don’t smoke; stop if you do.
- Lose weight if needed.
- Become more active.
- Identify and manage irregular, often rapid heart rate that commonly cause poor blood flow.
- Treat circulatory problems like peripheral artery disease, sickle cell disease, or severe anemia.
- Know and control your blood sugar and cholesterol.
- If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation.
- Adopt a healthy diet
- Know the warning signs of stroke (see “Stroke warning signs”) and respond immediately.
Some Stroke warning signs includes:
- Sudden numbness or weakness of the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body.
- Sudden confusion or trouble speaking or understanding.
- Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes.
- Sudden problem with walking, loss of balance, or coordination.
- Sudden, severe headache with no known cause.
In conclusion, Oxidative stress plays an important role in stroke causes. Free radical formation and subsequent oxidative damage may be a factor in stroke severity. Oxidative stress lead to toxicity and cell death with severe and potentially adverse consequences for the individual.
Antioxidants are molecules which help the brain cope with oxidative stress like Glutathione are therefore excellent candidates for stroke treatments and whether preventively or therapeutically.
Deficiency of Glutathione has been implicated as a critical factor in the stroke disease owing to its ability to help the body cope with oxidative stress.
CLICK HERE TO ORDER CELLGEVITY & MAX 3-5-7
With the right glutathione supplement, patients can potentially increase their brain’s concentrations of glutathione sufficiently to address stroke and its prevailing symptoms. In the meantime, patients can use glutathione supplementation to proactively protect their body from the ravaging effect of stroke.
Ribociene technology in cellgevity has been proven to be 300% more effective than the best alternative NAC.
So, raise your Glutathione level with Cellgevity today and empower your brains cells to take care of the toxins causing the chronic inflammation (oxidative stress) resulting in stroke disease in order to reverse the condition.